S3
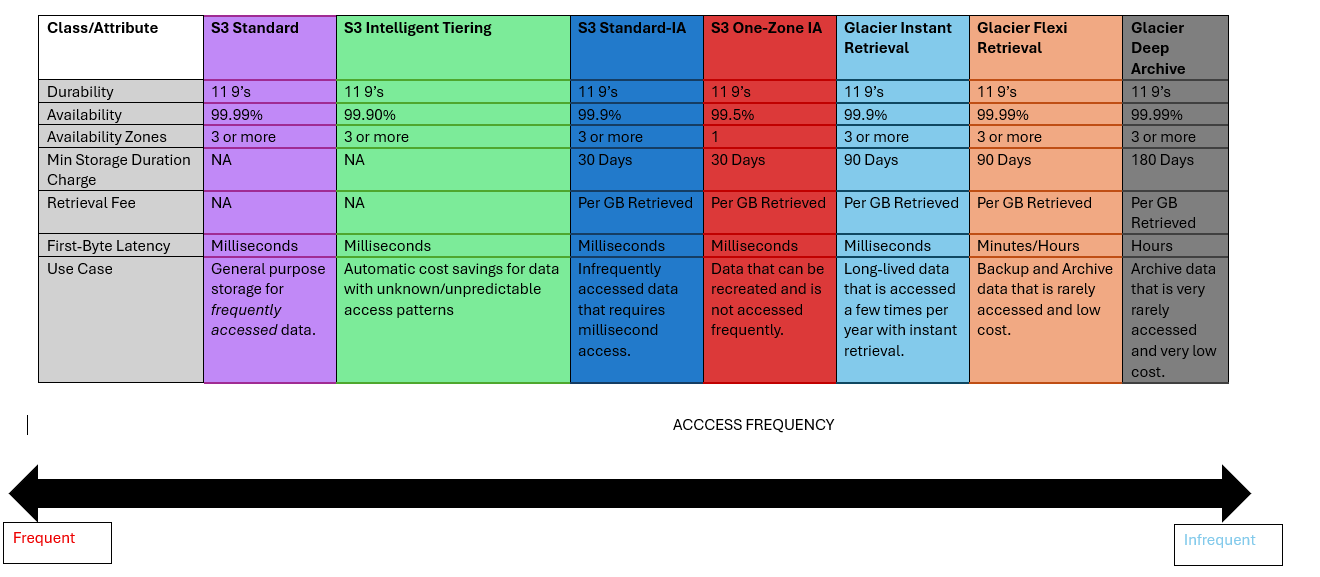
Below shows a quick summary of the S3 Storage Classes, note that the storage classes in S3 appear to be ever evolving and changing but these seem to be stable.
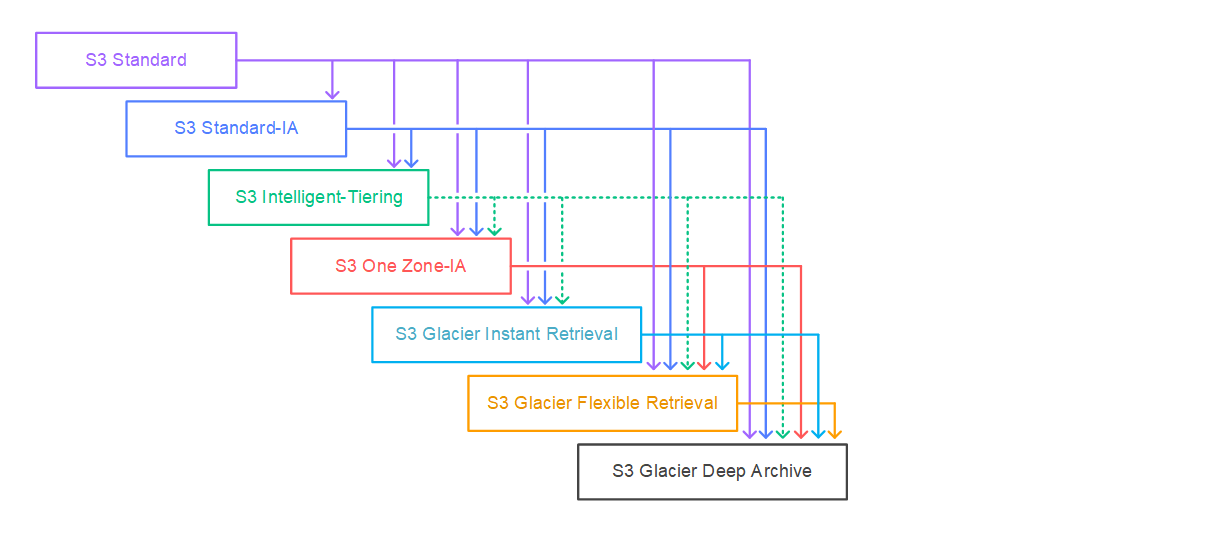
Object Transition Waterfall Chart:
Following on from above we can see the lifecycle transition policies for objects stored in each of these classes. Not all object storage classes can transition to another. Below is an image created by AWS used to describe the transitions that are possible.
Bucket Lifecycle Management:
- Transition Action: Defines when objects change classes, as above.
- Expiration Action: Define when objects are deleted.
Same/Cross Region Replication in S3:
S3 has a a SRR/CRR feature that allows one source bucket to replicate the objects stored to another bucket stored in a different region or within the same region;
- Automatic and Asynchronous replication
- Can be within one or multiple accounts
- CRR can be used for compliance, latency and operational efficieny reasons.
- SRR can be used for Aggregate Logs, test/prod environments, data laws.
- Both source and destination buckets must have versioning enabled.
Versioning:
When versioning is enabled on a bucket, objects that are deleted/updated are stored as entire new objects. The old version is still available within the bucket under a different 'Version'. You can then view the older version and swap back at any point if required. Deleting an object will place a delete marker on the object. You can then delete the delete marker to bring that image back in to the bucket.
Buckets
- Object Min size 0 Bytes
- Object Max size 5TB
- Unlimited object store
- Namespace has to be unique
- Regional Service
- Used with loads of other services such as CloudWatch Logs, EBS Snapshots, Storage Gateway etc.
- Can create resource policy to allow different services access
- Object based storage
Bucket Durability vs. Availability
| Durability | Availability |
| Protection against data loss/corruption. | Measurement of time data is available. |
| 11 9's durability. | 99.99% availability. |
Bucket Encryption:
- Encrypts by default using Server Side Encryption (SSE).
- Or you can choose to use SSE-KMS (Key Management Service).
- S3 Encrypts objects before saving to disk and decrypts when object downloaded.
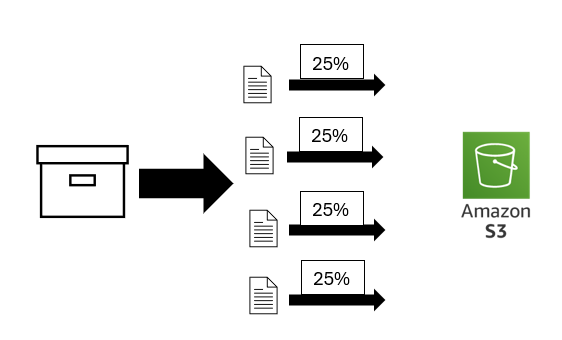
Multipart Upload:
- Upload objects in parts, independently and in any order.
- Performed using the S3 Multipart upload API.
- Recommended for objects >100MB.
- Can be used for files that are 5MB-5TB.
- Must be used for objects larger than 5GB.
- Helps to mitigate network issues.
S3 Transfer Acceleration: S3TA
- Uses CloudFront Edge Locations to improve performance of transfers from clients to S3.
- AWS only charges if it improves the performance.
- Enabled at Bucket level.
- Supposed to speed up 50-500%
- Moves faster over a longer distance.
- Used for uploading to and downloading from S3.
