Elastic Load Balancer
What is Elastic Load Balancer (ELB)?
An ELB is AWS version of a Load Balancer. It comes in three different varieties, Network, Application and the Gateway Load Balancer. Its purpose is to distribute 'load' between two or more endpoints. These endpoints can be EC2 Instances, Containers and IP Addresses. It also has built in functions to monitor the health of its registered targets and will only distribute traffic to healthy targets.
Application Load Balancer (ALB):
- Operates at request level and routes based on content of request (L7).
- Supports, path-based, host-based, string parameter and source ip based routing.
- Supports instances, IPs, Lambda and Containers as registered targets.
- Users listeners to check for traffic on specific protocol and port.
- Used with Web Apps and Microservice Architectures (Docker) or Lambda Targets.
- Billed per hour or partial hour (billed as full).
Network Load Balancer (NLB):
- Operates at connection layer and routes based on IP data (TCP/UDP etc L4).
- Ultra high performing, low latency and TLS offloading at scale.
- Can have a static IP and Elastic.
- Supports UDP and Static IP as targets.
- Supports cross-zone load-balancing.
- Used for TCP/UDP based applications
- Billed per hour or partial hour (billed as full).
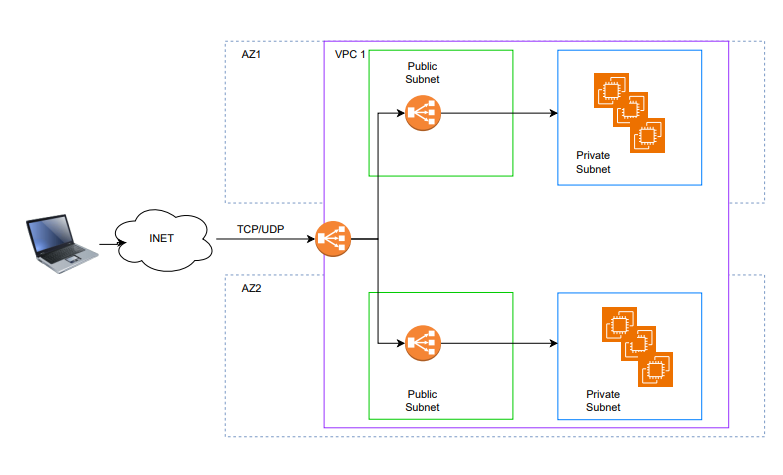
Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB):
- Operates at Layer 3 of the OSI model.
- Listens to all IP traffic on all ports and forwards based on the listeners.
- Enables deployment, scaling and mangement of virtual appliances (FW/IDPS)
- Provides a single entry and exit for all traffic (transparent network gateway).
- Billed per hour or partial hour (billed as full).
ELB Access Logs
- Disabled by default.
- Doesnt cost to enable.
- Logs stored in S3, cost for storage.
- Log files are encrypted and decrypted from S3 when accessed.
- Logs files every 5 minutes
- Information such as client IP addresses, request paths, time, connection time etc.
- Different log parameters for each ELB type.
- Essential for troubleshooting load balancer/backend issues.
Session State and Session Stickiness:
Sticky Sessions
- Cookie generated to tie user to same server so information such as Authentication or Basket items are kept on page refresh.
- If the instance or server is lost, the session is also lost. (Think about ASG).
Session State:
- Uses services such as DynamoDB or Elasticache to store session state information.
- Instances using ELB/ASG setup go to different service for session state.
- This means if the instance is terminated it doesnt matter, the state can be picked up on a new instance.
- ElastiCache is very popular for this service.
