AWS Systems Manager:
- Secure end-to-end management solution for resources on EC2, On-Prem and other clouds (Azure, Google etc).
- Hub for operations, management, app management, change management and node management.
- Can use the SSM Agent to manage EC2, On-Prem servers and VMs.
- IAM permissions are required to allow management.
- IAM Service role needed for hybrid solutions.
- AWS Systems manager is broken down in 7 different components.
1) Automation:
- YAML/JSON documents define a set of actions to perform.
- Use System Manager Automation to automate the task across AWS resources.
- Example: Document describes taking an RDS snapshot of a DB instance.
2) Run Command:
- Document types include command, automation, package etc
- Example: run command to check if updates are available to the OS of an EC2 fleet.
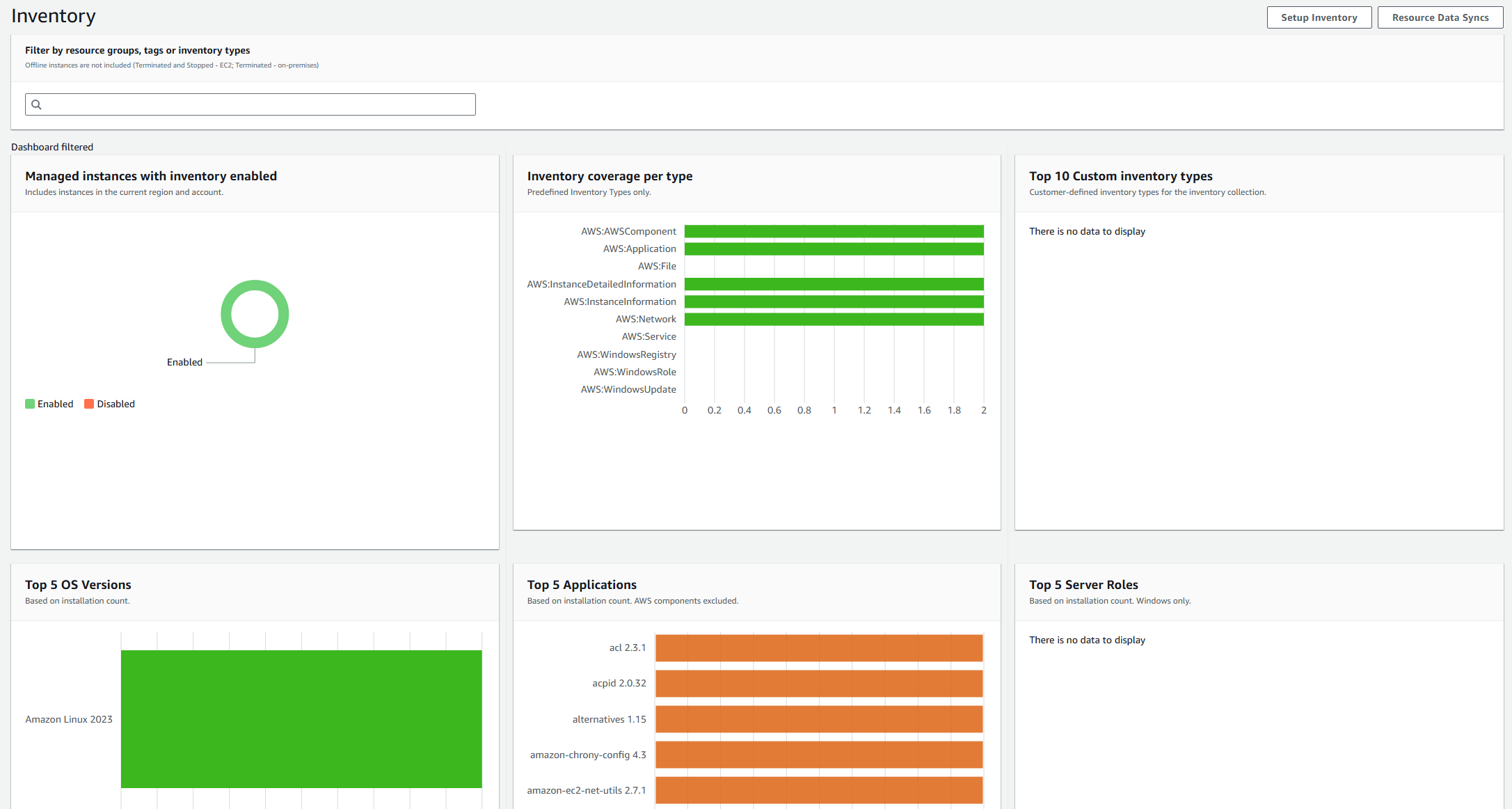
3) Inventory:
- Provides a dashboard graphical interface of devices, OS, Server Roles etc of all devices associated with the account.
4) Patch Manager:
- Select and deploy OS/Software patches automatically across a fleet of EC2/On-Prem instances.
- Patch baselines/rule base
- Schedule maintenance windows.
- Helps to ensure software is up-to-date and compliant.
5) Compliance:
- Scan for patch/config compliance.
- Collect aggregate data from multiple AWS accounts and regions.
- By default, AWS Systems Manager displays data about patching and associations.
- Can also customise service and create own compliance requirements.
6) Sessions Manager:
- Secure remote management of instances at scale without logging in to your servers.
- Replaces the need for bastion hosts, SSH or remote powershell.
- Integrates IAM for granular permissions.
- All actions recorded by CloudTrail.
- Can store session logs in S3 and output to CloudWatch Logs.
- Requires IAM permissions for EC2 instance to access SSM, S3 and CloudWatch Logs.
- Doesnt require any open ports to access devices.
7) Parameter Store:
- Secure heirarchical storage for config and secrets.
- Highly scalable, available and durable.
- Store data such as passwords, database strings and licence codes.
- Values can be plaintext or encrypted.
- Reference parameters by unique alias you create at the time of setting them up.
- No native rotation of Keys (unlike AWS Secrets Manager).


