Containers and Registries
What is a 'Container'?
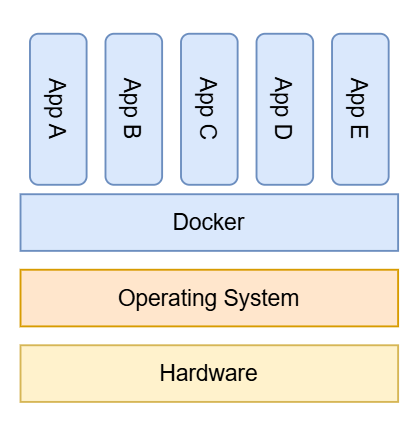
- A container is small compute environment with all resources required to run an app.
- Containers are usually small, efficient, incredibly fast and isolated.
- They are considered to be portable and scalable.
- Containers share a host OS but use Docker Engine to orchestrate.
- A Docker engine is software that runs above the host OS level that allows many containers to be run independently.
- Containers are built uisng from Docker Images, which is a text document called a Dockerfile.
- Use case: Microservices.
Elastic Container Service (ECS):
- Fully Managed service that allows orchestration of containers.
- Create, run and stop containerised applications from Docker.
- Windows Containers are supported too.
- ECS Clusters run multiple 'tasks' (Containers) and can be split across AZ's in a VPC.
- ECS can be serverless with Amazon Fargate.
- Elastic Load Balancer integration is common.
ECS Key Components:
| Component | Description |
| Cluster | Logical group of tasks/services. |
| Container Instance | EC2 instance running the ECS agent. |
| Task Definition | Blueprint for how a container should launch. |
| Task | Running container using setting of task definition. |
| Service | Defines long running tasks/How you want to autoscale and load-balance. |
**EC2 Container Instances must have the ECS agent installed and relevant IAM permissions to access it.
Elastic Container Registry (ECR):
- A private 'Dockerhub' for AWS.
- EC2/Docker pulls images from Dockerhub and upload the image to ECR.
- Integrated with ECS/EKS.
- Container images and artifcats are stored in S3.
ECR Components:
| Component | Description |
| Registry | Private registry provided to each AWS account. Create one or more repositories to store images. |
| Auth Token | Client must authenticate to ECR registries as an AWS user before being able to push/pull images. |
| Repository | Contains docker images, OCI images and Artifacts. |
| Repo Policy | Control access to repositories and images in them. |
| Image | Push/Pull container images in repositories. |
Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS):
- Managed service for running Kubernetes in the cloud or On-Prem.
- Kubernetes is an open source system for automating deployment, scaling and management of containerised applications.
- Kubernetes is used to standardise multiple environments and used mostly to scale out.
- EKS runs on EC2/Fargate and AWS Outposts.
- Groups of containers are called 'Pods'.
- Supports Autoscaling vertically and horizontally. (Pod resource vs Number).
- Supports Workload scaling: Cluster Autoscaling vs. Karpenter
- Cluster Autoscaling - Utilises autoscaling groups.
- Karpenter - Works directly with EC2 Fleet.
- Supports Network and Application Load-Balancers.
- Supports a Hybrid Deployment with Clusters On-Prem and in AWS Clous.
- Batch Processing allows you to Plan, schedule and execute batch workloads.
- Machine Learning: Use Kubeflow w/ EKS to model ML.
EKS Distro:
- Distribution of Kubernetes with same dependencies as Amazon EKS.
- Manually run Kubernetes Clusters anywhere without needing to worry about updates, compatibilities or versions across teams.
- Good for when Kubernetes run in multiple environments, on prem, AWS and other Clouds.
ECS/EKS Anywhere:
- Run and Manage ECS on your own On-prem infrastructure.
- Has to be supported by AWS.
- Uses SSM and ECS agent.
AWS Fargate:
- Serverless way to host ECS workloads.
- Run containers without having to provision or manage the backend.
- User has limited control in comparison to launching ECS with EC2.
ECS Launch Type Comparison:
| EC2 | Fargate |
| Explicitly provision instances. | Automatic. |
| Responsible for Upgrading/Patching. | Provisioned as needed. |
| Handle cluster optimisation. | Fargate handles automatically. |
| More granular control | Limited Control. |
External Launch type: Uses ECS Anywhere to host containers On-Prem.
