Elastic Cloud Compute
Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2): What is it?
In short, EC2 is AWS flagship compute service. It allows for a multitude of different hardware configurations for users to run compute in the cloud. It is also used as the underpinning for other applications such as RDS to use within AWS. The instances themselves are extremely customizable, scalable (in and out) and are ready to be launched within minutes. You can get them in many different pricing formats such as On-Demand, Reserved and Spot or different tenancies such as Dedicated Instance and Dedicated Host. These concepts are explored further below.
Amazon Machine Images (AMI):
- Image of software and settings used to setup and boot an EC2 instance.
- Must be compatible with the instance type you wish to boot.
- AMIs can be from AWS, Public/Shared and purchased from 3rd party providers in the marketplace.
- They are region specific.
- You can create an AMI from an instance as use it as a template for subsequent instances.
- Including configurations/apps in the AMI is called AMI Baking.
- Billed for Snapshots capacity of AMI not for creation itself.
Instance UserData:
- Can be found within Metadata service http://169.254.169.254/latest/user-data/.
- Userdata is used to execute commands upon the launch of an instance.
- Used for automated configuration tasks.
- Only run on first boot unless changed.
EC2 Instance Type:
- Two main categories of Hypervisor, Nitro-Based and Xen-Based.
- Nitro-Based Categories: General Purpose, Compute Optimised, Memory Optimised, Storage Optimised, Accelerated Computing, High-performance Computing.
- Xen-Based Categories: General Purpose, Compute Optimised, Memory Optimised, Storage Optimised, Accelerated Computing.
- Instance type should be selected based on the App/Service you wish to run.
- Nitro based computing allows for full use of host hardware accelerating Network operations and security.
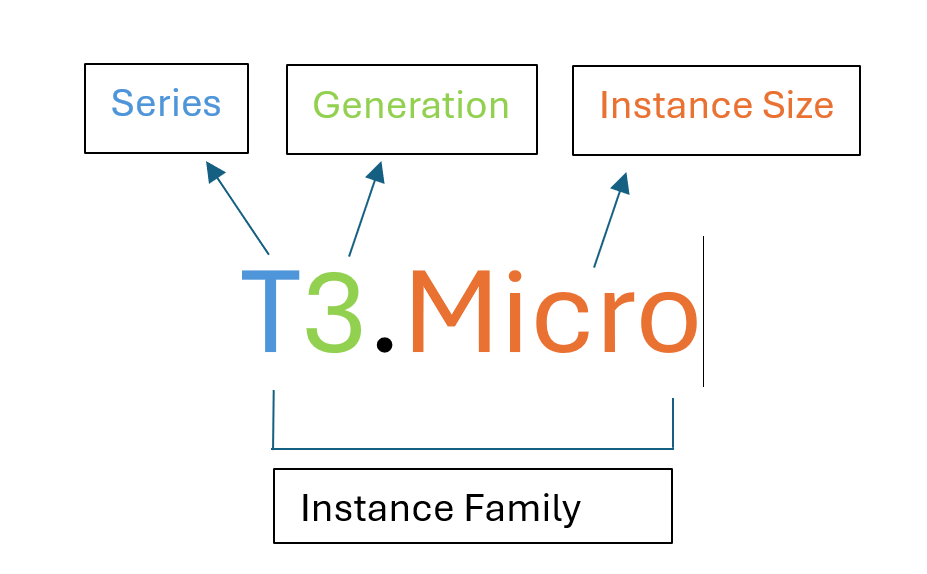
- Instance family and size dictates its cost and hardware capabilities such as, CPU cores, Memory, Storage options and Network Performance.
EC2 Pricing Models:
Functionally, all EC2 types are the same, the only difference is commitment and pricing. Naturally, the more you commit to using EC2 upfront, the less you pay/more savings you make. There are three different pricing models, On-Demand, Reserved and Spot.
On-Demand:
- Some instances optimised for EBS by default.
- Can be used with Capacity Reservation.
- Although rare, may not be available due to compute capacity.
- No commitment to savings plan.
- Could be used benchmark a workload before commitment.
- Used for unpredictable/fluctuating or extremely long workloads.
- Billed by Hour or Second.
Reserved:
- Discounted rate (<72%) at the cost of commitment 1 or 3 Years.
- Two types of reserved instance, Standard and Convertible.
- Can buy/sell standard scheduled reserved instances from marketplace.
- Convertible reserved instances can be exchanged for other attributes but not sold.
Spot:
- Neither on-demand nor reserved, think 'best-effort' availability.
- Can be re-claimed by AWS if compute is low in an AZ.
- Cheapest compute option.
- Can utilise a 'Spot Block' meaning the capacity wont be reclaimed 1-6Hrs.
- Spot Block comes at a cost.
EC2 Savings Plans
- Flexible Pricing model for EC2, Lambda and Fargate.
- Discounted only up to your commitment. Anything over is charged as standard.
- Savings up to 72% in exchange for usage commitment of instance type in a region. (T3 in US-EAST-1).
EC2 Placement Groups
Instances run on underlying hosts within an AZ. If the AZ goes offline, so does your instance. This could be problematic for some workloads that rely on these instances making them critical. Fortunately, AWS has thought of this and have 3 different placement groups for your EC2 instances.
Cluster:
- Logical grouping of instances within an AZ.
- Packs instances close together, not necessarily in same rack.
- Cant span multiple AZs.
- Low latency network performance
- Useful for High Performance Computing Apps.
Spread:
- Instances placed on distinct hardware.
- Good for apps with critical Instances.
- Spread between racks within an AZ.
- Max 7 instances per group per AZ in a region.
- Not supported for Dedicated Instances.
Partition:
- EC2 divided in to different partition groups reducing correlated failure.
- Each partition within placement group has its own rack.
- Isolate impact of hardware failure.
- Can be used for distributed and replicated workloads.
- Max 7 partitions per AZ.
