Relational Database Service (RDS)
RDS: Key Features
- A fully managed service - No provisioning, configuring, backing up or patching.
- RDS runs on EC2 instances - the user can choose the desired instance type.
- Relational = Structured Query Language.
- Used for Online Transactions Processes (OLTP) - Online Stores and Banking etc.
- RDS is scaled vertically (added resource to instance) unless we are scaling for database 'reads' then we scale horizontally.
- Supports many database engines including; Amazon Aurora, MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle and PostgreSQL.
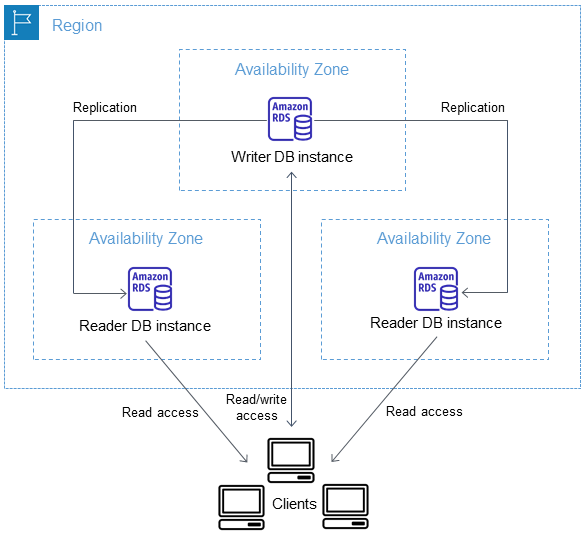
RDS: Multi-AZ Deployments (DB Instance and DB Cluster)
- Database Instance Deployment:
- 1 standby failover Database instance.
- Doesnt serve read-only traffic.
- Synchronous Standby replica.
- Sits in a different AZ within the same region.
- Database Cluster Deployment:
- 2 Standby failover read-only and one writer instance.
- Can serve read-only traffic.
- Despite its name the 'writer instance' can perform reads too.
- Spread across 3 different AZs.
- Semisynchronous replication which doesnt require confirmation that the replication has been successful from all replicas.
RDS: Security
- RDS Instances are always deployed to a VPC (default if you havent got one).
- Can have optional Public IP. (Not default)
- Should create Security Groups for the instance and Security Groups for Apps which need access.
- You should ensure apps use TLS/SSL to connect to the Database instance.
- Use the built in encryption feature for your Database, Snapshots, replicas and Backups at rest.
- Encyrption must be enabled at time of creation and cannot be undone.
- Tip: Can create a snapshot, encrypt the snapshot and spin up a new instance.
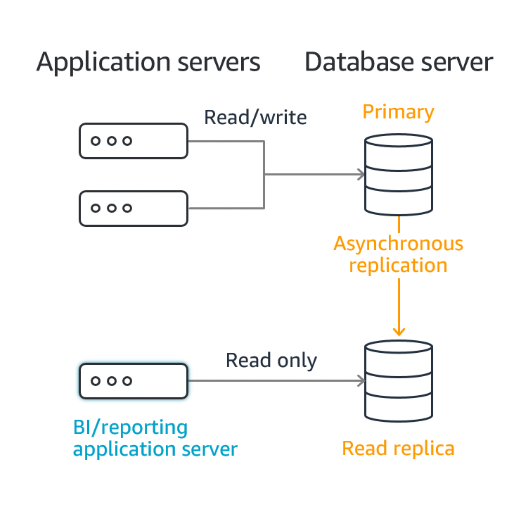
RDS: Read Replicas
- Used for improved performance and durability for RDS instances.
- Used to scale-out read-heavy workloads.
- Uses RDS native Asynchronous replication when a change is made to primary.
- Read-replicas hosted in same AZ.
- Any of the read-replicas can be promoted to a Primary if required.
- Most Database Engines allow for 15 read-replicas with exception of Oracle which allows 5.
RDS: Proxy
- Increases Fault Tolerance, Security and Scalability.
- Fully Managed.
- Sits in front of Database and creates many connection pools.
- Apps/Services connect to the Proxy and utilises a connection pool.
- The proxy works to reduce stress, share infrequent connections, implement high availability and control authentication methods.
RDS: Maintenance Window
- Separate to a Backup Window
- Used for Updating/Patching the OS/Database.
- Instance can go offline during this period.
- Weekly maintenance window configured by default but can be customised.
RDS: Backup and Recovery (Automated and Manual)
- Automated Backup:
- Setup a backup window at the time of creation, this mean no interruption.
- Backups and Logs (every 5mins) sent to S3.
- Retention period for backups are 0-35 days.
- Can restore from S3 but this creates a new instance.
- Database instance must be in 'Available' status to backup.
- Can replicate automatic backups to any region from S3.
- Manual Backup:
- Backs up the entire Database Instance and not the individual database.
- Single AZ Database Deployment will mean a short I/O suspension (Same for Automatic Backup method).
- Multi-AZ deployments will only mean a brief I/O suspension on primary node.
- Multi-AZ deployments for MariaDB, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL snapshots are taken from Standby nodes not the Primary.
- Snapshots do not expire which comes at a cost.
